Last weekend, I went searching for a bayou’s ghost.
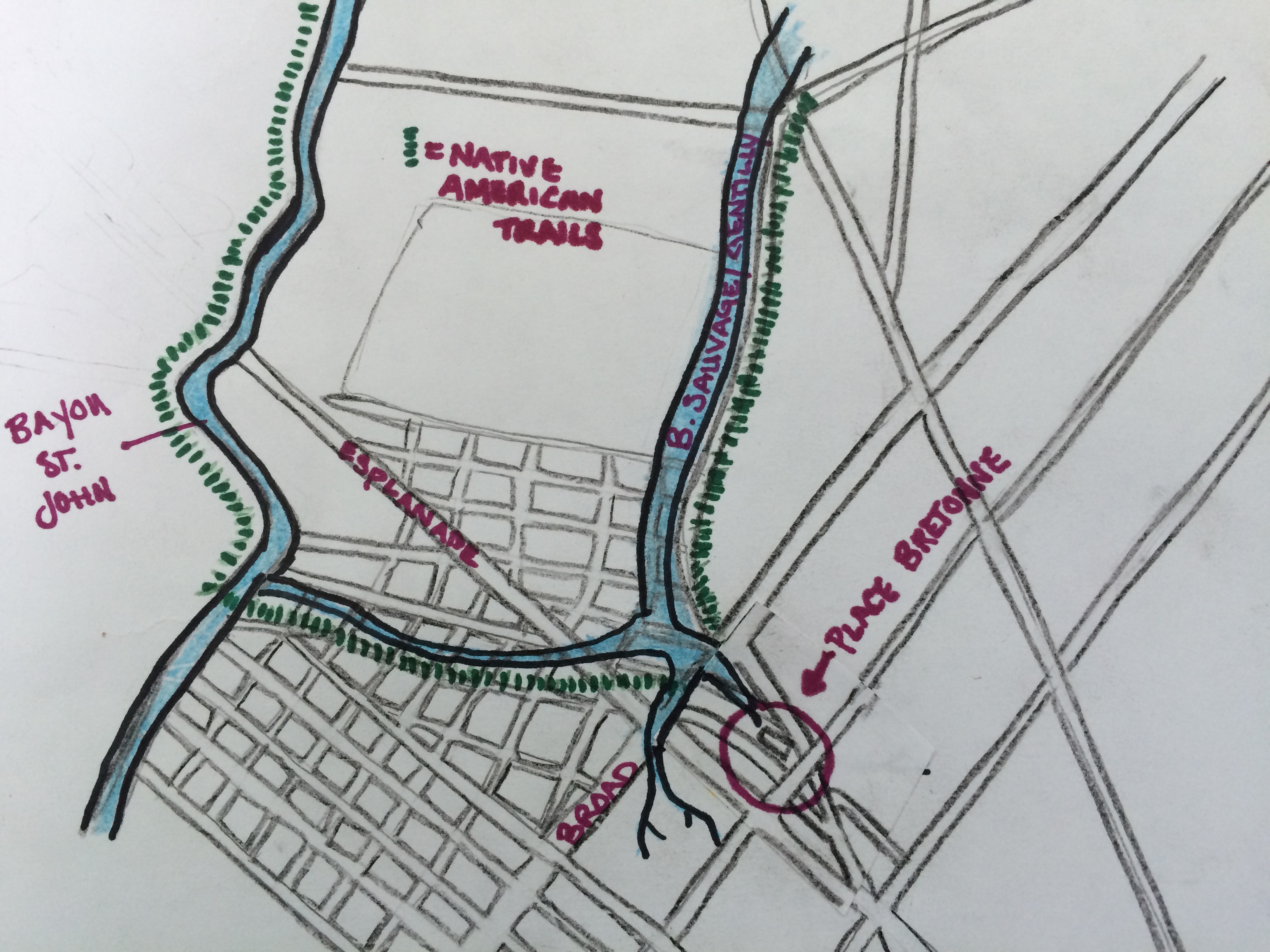
When the French arrived on the scene back at the end of the 17th century, a small trickle of water connected Bayou St. John with Bayou Gentilly—an even smaller, more sluggish slip of liquid, even more deserving of the term “bayou,” than the waterbodies it linked together. There was no indication that the waterway was used for navigation, or much of anything at all, but it appeared on early maps snaking along what would eventually become the heart of Faubourg St. John. Its claim to fame might have been that the old portage route followed its basic arc from Bayou St. John to Bayou Gentilly (to the site of the Place Bretonne Indian market) before continuing on its way toward the present-day French Quarter.

map by author, used in previous post on Place Bretonne
The official name of this bayou (I’ve come across several), and when exactly it got filled in, remain a mystery. But during an interview with a Faubourg St. John resident, I was told that a slight declivity along N. Dupre street marks the old trench of this long-forgotten bayou. And, of course, I wanted more—I wanted to trace the ghost-bayou’s bed from start to finish!
Alas, the results of my adventure through the neighborhood are not all that impressive. Nothing definitive. No ghost-bayous jumping out to spook me. Just small dips along the relevant roadways that may or may not have anything to do with said trickle of yesteryear. As any New Orleanian knows, irregularities in the elevation of the city’s streets are not exactly rare….
I walked from Moss to Crete streets, zig-zagging between DeSoto and Bell along Hagan, N. Rendon, N. Lopez, N. Gayoso, N. Dupre, and N. White—searching all the while for indications of the ghost-bayou’s wanderings.
It is said that the bayou broke off from Bayou St. John around present-day 1222 Moss Street. It’s as if the house itself—hiding behind its lush foliage—seeks to hide its watery underpinnings….

photo by author

photo by author
Does this puddle along Hagan Avenue indicate a bayou-related dip?

photo by author
What about this driveway’s slope on N. Rendon?

photo by author
Or this mansion’s sunken drive?

photo by author
Is it just me, or does N. Lopez look a little concave right here? (My dog’s second photobomb…he was helping me look.)

Photo by author
What about here? The slightest of dips along N. Dupre….

photo by author
Here is the clearest indication of the ghost trench (shown to me by the same Faubourg St. John resident mentioned above), where Crete meets Esplanade.
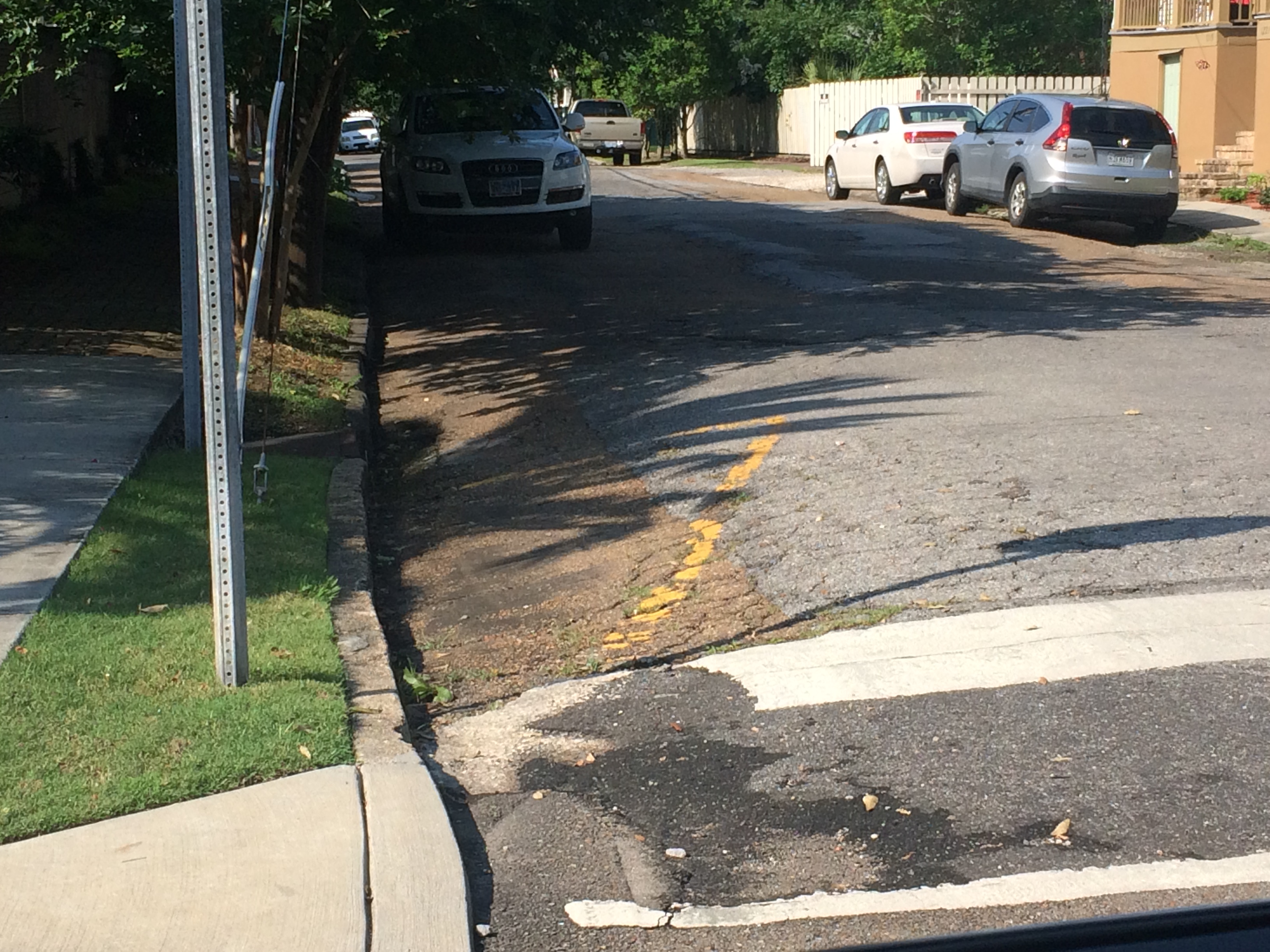

Ok, like I said, nothing too terribly amazing. But was the journey worth it? You bet! And maybe someone reading this post will have their own bayou ghost story to share, and will tell us all where to look next time we’re in the neighborhood….